Sebaceous gland hyperplasia
OVERVIEW
What is sebaceous hyperplasia?
Sebaceous hyperplasia is a benign condition caused by the enlargement of normal sebaceous glands in the skin. Its primary feature is the increase in size and number of sebaceous gland structures near hair follicle openings. The main manifestation is small facial papules, typically 1–3 mm in diameter and pale yellow in color.
Is sebaceous hyperplasia common?
Sebaceous hyperplasia is very common in newborns. Nearly half of full-term newborns exhibit it, while the occurrence rate is slightly lower in premature infants. In adults, sebaceous hyperplasia is relatively uncommon.
What are the types of sebaceous hyperplasia?
There are two types of sebaceous hyperplasia: neonatal sebaceous hyperplasia and senile sebaceous hyperplasia. Neonatal sebaceous hyperplasia occurs within weeks after birth, while senile sebaceous hyperplasia generally affects middle-aged and elderly individuals. The manifestations of these two types differ significantly.
SYMPTOMS
What are the common manifestations of sebaceous gland hyperplasia?
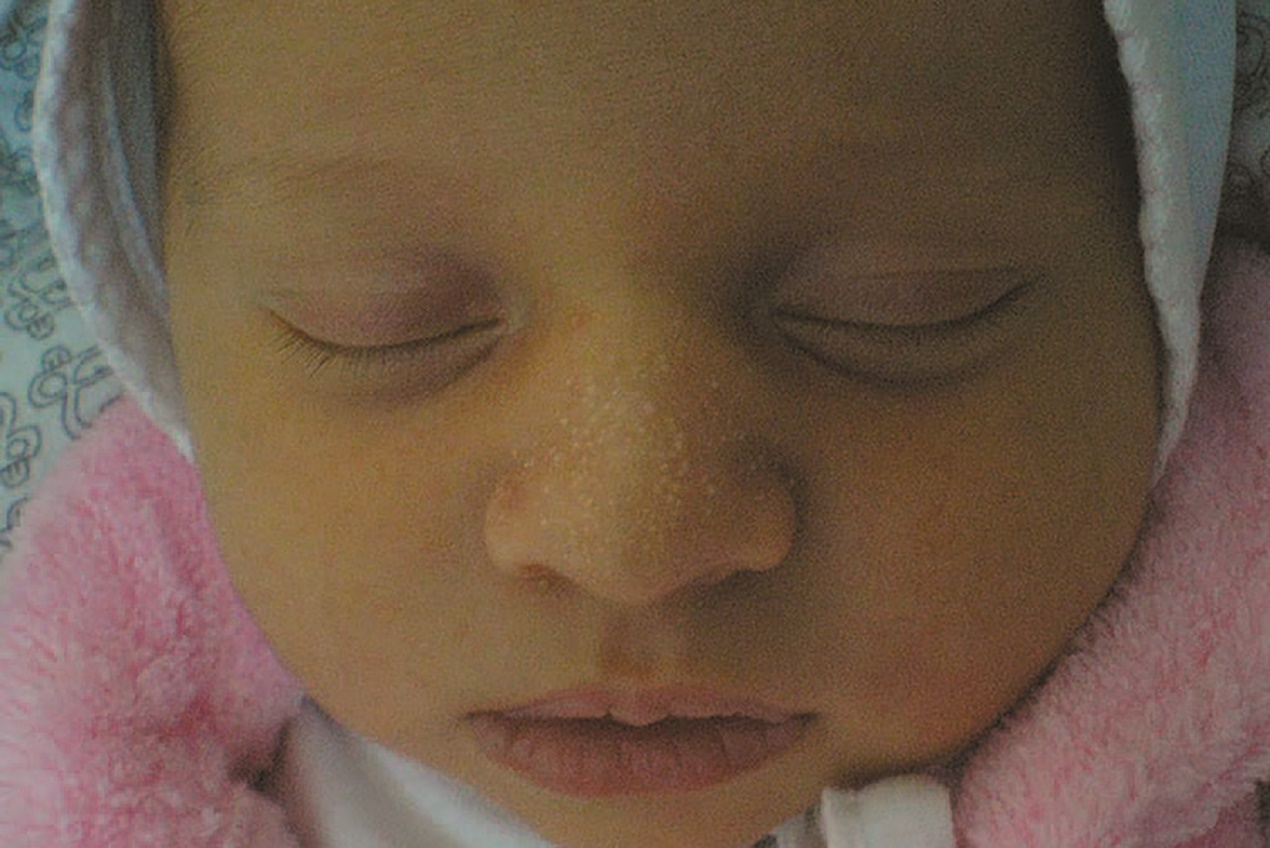
In newborns, rashes caused by sebaceous gland hyperplasia tend to occur in areas with the highest concentration of sebaceous glands, particularly the nose, as well as around the upper lip, chin, and cheeks.
The rashes are small and numerous, primarily consisting of yellow granules (papules) measuring 1–2 mm. They may cluster into small patches without central dimpling.
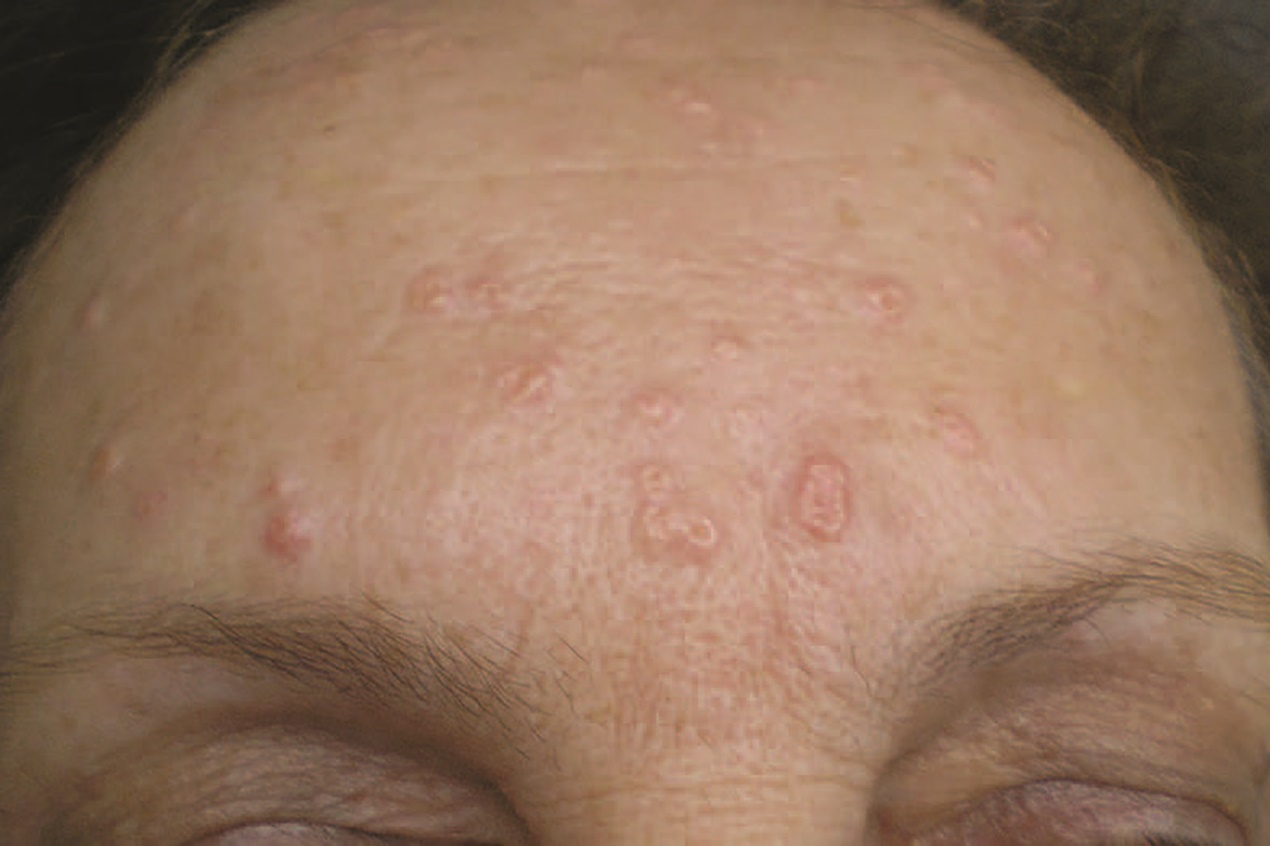
In adults, sebaceous gland hyperplasia may present as single or multiple lesions, commonly on the forehead and cheeks. They are usually scattered, appearing as raised granules, sometimes lobulated, with a diameter of 2–3 mm (up to 5 mm).
The texture is soft, and the color ranges from pale yellow to yellow. The center of the lesion often has a depression, sometimes accompanied by telangiectasia. There is no itching or pain.
Sebaceous gland hyperplasia may occasionally present with a distinctive feature called a "string of pearls," caused by linear arrangements of hyperplastic sebaceous glands, typically appearing on the neck or near the collarbone.
Where does sebaceous gland hyperplasia commonly occur?
In newborns, it most frequently affects the nose. In adults, it most commonly appears on the forehead and face.
How does sebaceous gland hyperplasia progress?
In newborns, it usually resolves on its own within weeks without leaving marks. In adults, the lesions may gradually increase in number and size or remain stable over time. It is not contagious and does not resolve spontaneously.
What complications can arise from sebaceous gland hyperplasia?
Sebaceous gland hyperplasia is a benign minor skin condition and generally does not lead to other new issues.
CAUSES
What are the common causes of sebaceous gland hyperplasia?
In newborns, the cause of sebaceous gland hyperplasia is the temporary increase in androgen levels due to maternal androgens crossing the placenta into the baby's body. Androgens stimulate the hyperplasia of sebaceous glands.
In adults, the exact underlying cause of sebaceous gland hyperplasia is unclear. The formation of skin lesions may be related to prolonged sun exposure, trauma, chronic local inflammatory stimulation, or the use of immunosuppressants (such as cyclosporine). The final manifestation is an increase in normal sebaceous glands.
Who is more likely to develop sebaceous gland hyperplasia?
In newborns, sebaceous gland hyperplasia is common in full-term infants, with almost no gender difference. The incidence is slightly lower in premature newborns.
In adults, it is more common in middle-aged and elderly individuals, hence it is also referred to as senile sebaceous gland hyperplasia.
Is sebaceous gland hyperplasia a tumor?
Sebaceous gland hyperplasia is not a true tumor but a benign enlargement of the sebaceous glands.
Is sebaceous gland hyperplasia hereditary?
Sebaceous gland hyperplasia is almost never hereditary. In rare cases, it may be a manifestation of Muir-Torre syndrome, a rare genetic disorder that increases the risk of certain cancers.
DIAGNOSIS
How is sebaceous hyperplasia diagnosed?
It mainly relies on a dermatologist's in-person examination of the skin. If typical manifestations of sebaceous hyperplasia are present, a diagnosis can be made.
Typical manifestations include small yellow granules on the face. In infants, the center of the rash is not sunken, while in adults, the center is slightly sunken, with no itching or pain.
What tests are needed to diagnose sebaceous hyperplasia?
Newborn sebaceous hyperplasia rarely requires additional tests. For adults, if the diagnosis is unclear, a dermatoscopy or pathological examination may be needed.
Dermatoscopy is a special magnifying tool that allows observation of deeper skin lesions. The main features of sebaceous hyperplasia include a pale yellow background, clear boundaries, pale yellow lobulated structures, and irregular branching blood vessels around the lesion.
A pathological examination involves a minor surgical procedure (skin biopsy) in a dermatology clinic. The removed lesion is made into a pathological slide and examined under a microscope for detailed analysis.
The pathological manifestation is a group of enlarged sebaceous glands surrounding the hair follicle, called sebaceous lobules. These lobules consist of mature sebaceous cells and open together onto the skin's surface.
What diseases can sebaceous hyperplasia be confused with? How to differentiate them?
Sebaceous hyperplasia is often confused with conditions such as Fordyce spots, syringomas, and flat warts.
-
Fordyce spots are small, pinhead-to-millet-sized dots, pale yellow or whitish, sometimes slightly raised. They are uniform in size and vary in number. When numerous, they may cluster together. They commonly appear on the lip mucosa and genital mucosa and cause no discomfort.
-
Syringomas are benign tumors often found on the eyelids and cheeks. They appear as small, hard granules with no central depression. They rarely resolve on their own but do not become malignant.
-
Flat warts are a viral skin condition. They are usually scattered and appear on the face or hands. The rash consists of flat, soft granules with a smooth top, typically pale brown. They can easily spread to other skin areas.
Differentiation is mainly based on age, rash location, and specific details of the rash. A comprehensive assessment is made, and if necessary, dermatoscopy or pathological examination may be performed.
TREATMENT
Which department should I visit for sebaceous hyperplasia?
Dermatology.
Can sebaceous hyperplasia resolve on its own?
Sebaceous hyperplasia in newborns can resolve spontaneously, taking several weeks to disappear. In adults, sebaceous hyperplasia persists long-term and does not resolve on its own.
How is sebaceous hyperplasia treated?
Newborn sebaceous hyperplasia requires no treatment at all.
Adult sebaceous hyperplasia generally does not require treatment. If it affects appearance and cosmetic improvement is desired, options like cryotherapy, laser therapy, or surgical excision may be considered. Long-term topical use of retinoids may also have some effect in certain cases.
Is hospitalization required for sebaceous hyperplasia?
No hospitalization is needed.
What are the common side effects after treatment for sebaceous hyperplasia?
After cryotherapy or laser treatment, localized hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation may occur. Surgical excision may leave some degree of scarring.
Can sebaceous hyperplasia be cured?
As mentioned earlier, newborn sebaceous hyperplasia can resolve without treatment.
Adult sebaceous hyperplasia can generally be effectively treated with cryotherapy, laser therapy, or surgery, achieving a cure. However, recurrence in other areas cannot be completely prevented after treatment.
DIET & LIFESTYLE
What should patients with sebaceous hyperplasia pay attention to in their diet?
Sebaceous hyperplasia is unrelated to diet. Maintain a normal diet in daily life without the need for specific restrictions.
What should patients with sebaceous hyperplasia pay attention to in daily life?
Monitor changes in skin lesions. If there is a noticeable increase in number or size within a short period, or symptoms like itching or pain occur, seek medical evaluation promptly.
What precautions and care are needed after treatment for sebaceous hyperplasia?
After treatment, maintain local cleanliness to prevent infection and avoid frequent friction. Sun protection in the short term can help reduce the risk of pigmentation. Follow up as instructed by the doctor to assess whether the condition is fully resolved.
Does sebaceous hyperplasia require follow-up examinations? How are they conducted?
A follow-up examination can be scheduled 3–4 weeks after treatment to evaluate effectiveness. The doctor will typically assess visually, though dermatoscopy may occasionally be used.
PREVENTION
Can Sebaceous Gland Hyperplasia Be Prevented? How?
There are no effective preventive measures for neonatal sebaceous gland hyperplasia. Some perspectives suggest that adult sebaceous gland hyperplasia may be related to trauma and local chronic inflammatory stimulation. In this regard, avoiding prolonged sun exposure, trauma, and local dermatitis or eczema may be somewhat helpful.
How to Prevent the Recurrence of Sebaceous Gland Hyperplasia?
Neonatal sebaceous gland hyperplasia does not recur.
For adults, preventing recurrence mainly involves seeking proper treatment from a doctor at a reputable hospital and avoiding reliance on folk remedies, "miracle drugs," or other non-standard treatment methods.
How Can Patients with Sebaceous Gland Hyperplasia Prevent Complications?
Sebaceous gland hyperplasia does not lead to other new issues and has no complications.
